Why in News?
- India has raised objections to China’s construction of a mega dam on the Brahmaputra River and Beijing’s decision to create new administrative counties in Aksai Chin, a disputed territory.
- This development has escalated concerns over water-sharing issues and territorial integrity, particularly given the Brahmaputra’s significance for India and Bangladesh as lower riparian states.
Introduction
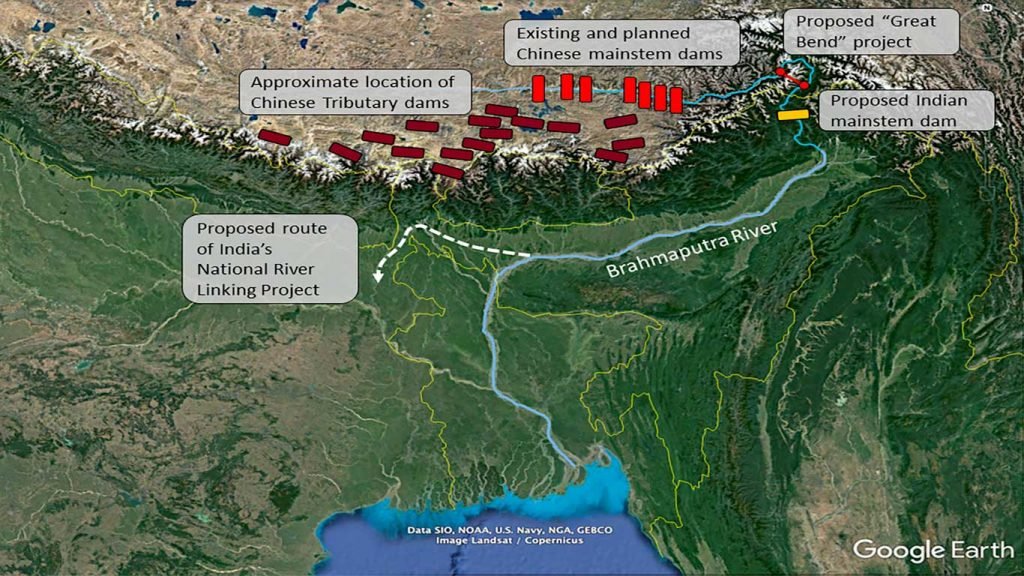
- China’s decision to build the world’s largest dam on the Brahmaputra River in Tibet, close to the Indian border, has drawn strong reactions from India.
- India has expressed its concerns over the potential impacts on downstream states and the lack of prior information about the project, which violates established conventions.
- Additionally, Beijing’s move to create new administrative counties in Aksai Chin has further complicated Sino-Indian relations.
Key Highlights
Brahmaputra Dam Project
Scale of the Project:
- The proposed dam will be the largest hydropower project in the world, estimated to cost $137 billion.
- It will be constructed on the Brahmaputra River in Tibet, close to the Indian border.
Concerns Raised by India:
- India was not informed about the dam, learning of it through media reports, despite a bilateral convention requiring prior notification.
- Concerns were conveyed to China regarding the potential harm to downstream riparian states, particularly India and Bangladesh.
Potential Impacts:
- The dam could disrupt water flow and adversely affect ecosystems and agricultural activities in India and Bangladesh.
- It may also lead to disputes over water sharing and raise geopolitical tensions in the region.
China’s New Counties in Aksai Chin
Aksai Chin Dispute:
- Aksai Chin is a disputed region claimed by India as part of Ladakh but controlled by China.
- Beijing’s establishment of new administrative counties in the region has raised sovereignty concerns.
India’s Stand:
- India has reiterated that Aksai Chin is an integral part of its territory and objected to China’s actions.
- These developments come amidst strained relations following the Galwan Valley clashes in 2020.
Key Terms and Definitions
Brahmaputra River
- Also known as Yarlung Tsangpo in Tibet, it originates in the Tibetan Plateau and flows through India and Bangladesh.
- It is a major river system for the region, supporting agriculture, livelihoods, and biodiversity.
Riparian States
- Countries or regions through which a river flows.
- In this case, India and Bangladesh are lower riparian states of the Brahmaputra, while China is the upstream state.
Hydropower Project
- Large-scale dams built for generating electricity by harnessing the energy of flowing or falling water.
- Hydropower projects can alter river flow, impact ecosystems, and affect water availability downstream.
Aksai Chin
- A region in the Ladakh Union Territory, claimed by India but controlled by China.
- The area remains a core territorial dispute between the two nations.
India’s Concerns Over the Brahmaputra Dam
Violation of Conventions
- India emphasized that China failed to notify about the dam project, which is a breach of the existing bilateral understanding on sharing river information.
Geopolitical Tensions
- The Brahmaputra flows through multiple countries, and unilateral actions by China could increase regional tensions.
Environmental and Social Impacts
- The project threatens to disrupt:
- Water supply for irrigation and drinking.
- Fish migration and aquatic ecosystems.
- Livelihoods dependent on the river.
Strategic Implications of the Aksai Chin Issue
Territorial Sovereignty
- The creation of new counties in Aksai Chin reflects China’s attempts to strengthen its control over the disputed region.
- India’s objections reiterate its claim over the territory.
Impact on India-China Relations
- These actions deepen mistrust and complicate efforts to resolve border disputes.
- They follow ongoing military standoffs and diplomatic challenges in the region.
Conclusion
- Why This News is Important:
- The Brahmaputra dam project and developments in Aksai Chin are critical issues for India’s territorial integrity and water security.
- Both raise concerns about China’s unilateral actions, which could set precedents for other shared river systems and disputed territories globally.




