China’s Brahmaputra Hydropower Project
India’s Water Security and Strategic Concerns – CLAT Current Affairs 2026
Why in News?
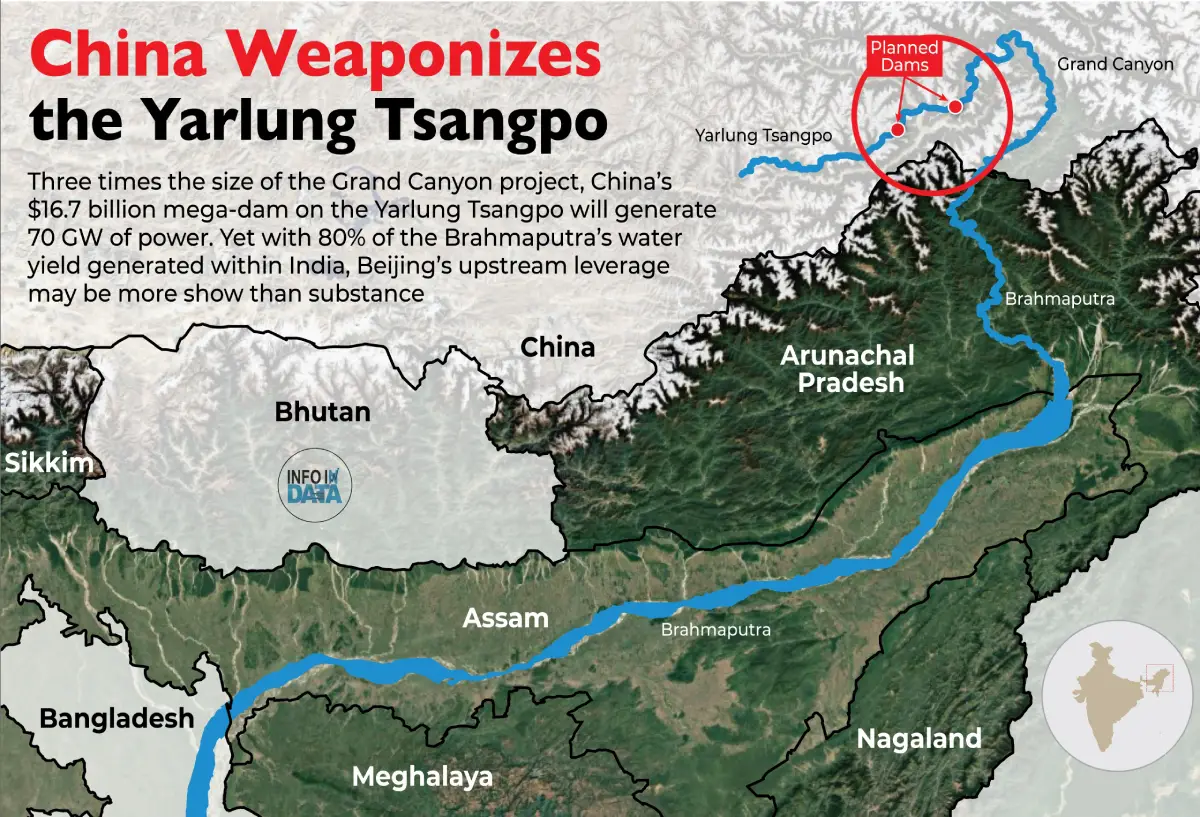
China has initiated construction on a massive $170 billion hydropower project on the Yarlung Zangbo river (called Siang in Arunachal Pradesh and Brahmaputra in Assam), just before it bends into India. This development has triggered major strategic and environmental concerns in India and Bangladesh, especially related to flooding, water security, and storage infrastructure in India’s Northeast. The project is expected to generate 60 GW of power—almost three times the Three Gorges Dam’s capacity—making it a significant geopolitical and environmental development.
This issue directly concerns India’s hydro-diplomacy, environmental law, strategic policy, and transboundary water governance, making it vital for CLAT Current Affairs 2026.
Introduction
Water is no longer just a natural resource—it is a strategic asset. The recent Chinese initiative to build a mega-dam on the Yarlung Zangbo, close to India’s border, has heightened India’s longstanding concerns over the Brahmaputra River’s flow, flood risks, and hydroelectric potential. The Brahmaputra is one of India’s major transboundary rivers, originating in China and flowing through Arunachal Pradesh and Assam before entering Bangladesh.
While bilateral talks between India and China have taken place in the past (including a 2013 MoU for sharing hydrological data), the lack of transparency from Beijing, coupled with India’s slow response in developing countermeasures, has made the situation increasingly precarious. Experts now call for immediate action to establish storage and dam infrastructure downstream to mitigate any potential disaster and secure India’s energy future.
This development is critical for CLAT aspirants to understand the intersection of international law, river water treaties, environmental ethics, and strategic policy, especially under the lens of Article 21 (Right to Life), Article 262 (Inter-State River Water Disputes), and environmental jurisprudence.
Point-wise Summary
🔹 1. China’s New Hydropower Project on the Yarlung Zangbo
- Location: Just before the Yarlung Zangbo enters India as the Siang river in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Capacity: Expected to generate 60 GW of electricity, three times more than China’s Three Gorges Dam.
- Cost: Estimated at $170 billion.
- Purpose: Part of China’s development agenda for the Tibetan region.
🔹 2. Concerns for India and Bangladesh
- Arunachal CM Pema Khandu called the Chinese project a “ticking water bomb”.
- Fears include:
- Sudden surges in water flow due to unannounced releases.
- Disruption of downstream water supply.
- Changes in sedimentation patterns.
- Risks of flash floods and environmental instability.
🔹 3. Vulnerabilities of the Brahmaputra Basin
- The Brahmaputra gains volume primarily after entering India, unlike other Himalayan rivers.
- Main tributaries like the Lohit and Dibang also flow in India.
- Its changing river path and unpredictable floods make it highly vulnerable.
- Over 80% of India’s hydro-potential in the Northeast remains untapped.
🔹 4. Climate and Ecological Risks
- Climate change is already accelerating glacier melt in the Eastern Himalayas.
- The Chinese dam could worsen:
- Erosion and sedimentation in Assam.
- Inundation during monsoons.
- Potential water scarcity in dry seasons.
🔹 5. India’s Delayed Strategic Response
- India has not yet built any major storage dam on the Brahmaputra.
- In 2017, the idea of building a dam at Yingkiong was still in planning.
- NITI Aayog later proposed a project at Siang for flood mitigation and energy storage.
- Work on the Jal Shakti-backed Siang Dam is still pending pre-feasibility reports and clearances.
🔹 6. Bilateral Arrangements with China
- India and China signed a MoU in 2013 to share hydrological data.
- No binding treaty exists like the Indus Waters Treaty with Pakistan.
- China often withholds data, especially during monsoons or conflict periods.
🔹 7. Importance of Strategic Dams in the Northeast
- Experts suggest storage-based projects should be built as a buffer against Chinese manipulation.
- These dams could:
- Reduce downstream flooding.
- Enable controlled water use for irrigation and hydropower.
- Enhance energy access in the Northeast.
- Boost inter-basin transfer feasibility during water crises in other states.
🔹 8. Hydrological Complexity of the Region
- The Eastern Himalayas are geologically fragile and seismically active.
- Building dams requires:
- Risk modeling of earthquakes and landslides.
- Environmental Impact Assessments (EIA).
- Community rehabilitation frameworks.
🔹 9. Local Impact: Displacement and Livelihood Loss
- Indigenous tribes, forest dwellers, and farming communities could be affected.
- Livelihoods tied to seasonal agriculture and fishing.
- Previous large dams (e.g., Subansiri) faced heavy protest due to ecological imbalance.
🔹 10. The Need for Urgent Government Action
- Political consensus is now building around the need to:
- Expedite dam construction.
- Enforce interstate coordination.
- Strengthen hydrological surveillance.
- Enhance diplomatic engagement with China.
- Experts argue India’s response must not be reactive, but anticipatory and proactive.
Explanation of Key Terms
Term | Explanation |
Yarlung Zangbo | The upper stream of the Brahmaputra River flowing through Tibet. |
Three Gorges Dam | World’s largest hydropower project on the Yangtze River in China. |
Hydropower | Electricity generated using water flow, especially from rivers and dams. |
MoU | Memorandum of Understanding – a non-binding agreement between two countries. |
EIA | Environmental Impact Assessment – mandatory study before starting large infrastructure projects. |
Sedimentation | Accumulation of sediments that affects water flow and quality. |
Inter-basin Transfer | Shifting water from surplus to deficit basins. Can be used for managing droughts or urban supply. |
Riparian State | A country or region situated along the banks of a river. |
Relevance for CLAT 2026 Aspirants
Legal Reasoning
- May be linked to:
- Right to Water under Article 21.
- Transboundary environmental harm and no-harm principle in international law.
- PILs and court interventions on dam safety and displacement.
- Inter-State Water Disputes (Article 262).
Current Affairs
- Ideal for passage-based MCQs in the CLAT GK section.
- Important themes:
- India-China Relations
- Environmental Diplomacy
- Climate Adaptation Strategy
Static GK Integration
- Connects to:
- Brahmaputra River system
- Major rivers of India and their international links
- Indus Waters Treaty vs Brahmaputra situation
Conclusion
China’s mega-dam construction on the Yarlung Zangbo represents more than an infrastructure project — it is a geostrategic, environmental, and humanitarian challenge for India. The time for reactive diplomacy has passed, and India must now urgently implement countermeasures, such as dam building, inter-basin water storage, and diplomatic engagement to safeguard its riverine ecosystems, border security, and energy future.
For CLAT 2026 aspirants, this article offers insight into how international relations, constitutional rights, and environmental law are intricately woven into issues of national security and sustainable development.
This Blog is Powered by CLAT Gurukul — India’s Leading Law Entrance Prep Platform
At CLAT Gurukul, we believe in empowering future legal minds with the right blend of knowledge, strategy, and mentorship. This blog is a reflection of our commitment to quality content that not only helps aspirants stay updated but also sharpens their conceptual clarity.
Why CLAT Gurukul?
- Personalized Mentorship by Top Legal Educators
- Comprehensive Study Materials & Legal Updates
- Daily Practice Sets, Mocks & Performance Tracking
- Result-Oriented Strategy for CLAT, AILET, and CUET
Whether you’re reading this article to deepen your understanding or to stay ahead in your exam prep — you’re already one step closer with CLAT Gurukul by your side.
Join thousands of successful aspirants who trusted CLAT Gurukul and cracked India’s top law entrance exams.
Visit https://www.youtube.com/@CLATGurukul/shorts to learn more or speak to our experts now!
Note from CLAT Gurukul
At CLAT Gurukul, we are committed to providing free CLAT study material, including CLAT current affairs, legal reasoning practice sets, general knowledge updates, logical reasoning questions, English comprehension exercises, and more — all curated by top mentors.
Our blog section is regularly updated with high-quality CLAT content tailored to match the evolving pattern of the CLAT UG exam. Whether you’re looking for CLAT 2026 current affairs, CLAT legal reasoning passages, or mock practice sets, we have you covered.
We believe in open-access learning and will continue to publish free CLAT preparation resources to help serious aspirants succeed.
Explore more free content under categories like:
Best online coaching for CLAT, CLAT current affairs, CLAT GK updates, CLAT legal updates, CLAT logical reasoning, and CLAT English preparation.
For structured learning, daily mocks, and expert mentorship, visit https://www.youtube.com/@CLATGurukul/shorts — the Best CLAT Coaching in Patna and India’s most trusted platform for CLAT online coaching.




