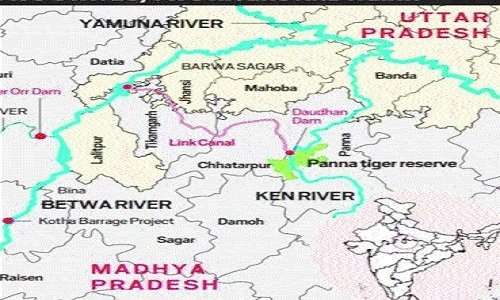
This document provides an in-depth analysis of the Ken-Betwa River Linking Project and India’s developmental aspirations while addressing critical environmental concerns. The content is tailored for competitive exam preparation, highlighting essential facts and concepts.
Introduction
- The Ken-Betwa River Linking Project is India’s first major river-interlinking initiative among 16 proposed projects.
- Ceremonially inaugurated recently after 29 years of conception.
- Sparks debate between development and environmental conservation.
- This project serves as a lens to understand the challenges of balancing economic progress with preserving ecological integrity.
India’s Core Development Priorities
Infrastructure Development
- World-class infrastructure aims to:
- Enhance productivity.
- Facilitate trade.
- Attract investments.
- Key initiatives:
- National Infrastructure Pipeline: ₹111 lakh crore over 5 years.
- Gati Shakti Plan: Integrates sectors and improves connectivity.
- 2023-24 Capital Expenditure Allocation:
- Raised to ₹10 lakh crore (3.3% of GDP).
Climate Change Mitigation and Renewable Energy
- Transitioning to renewable energy for reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Green Hydrogen Mission: Budget of ₹19,700 crore.
- India’s renewable energy capacity:
- 201.45 GW (46.3% of total installed capacity).
- Progress aligns with Paris Agreement Commitments.
Human Capital Development
- Focus on education and healthcare for socio-economic transformation:
- PM e-Vidya Scheme expanded digital education.
- Ayushman Bharat covers 50 crore citizens under health insurance.
- Literacy rate: 77.7%.
- Infant Mortality Rate (IMR): 28 per 1000 live births in 2020.
Digital Economy Expansion
- UPI Transactions:
- 172 billion in 2024, up 46% from 2023.
- Jan Dhan Yojana:
- 53 crore unbanked individuals brought into the system.
Employment and Rural Empowerment
- PM Vishwakarma Yojana:
- Budget of ₹13,000 crore to support artisans.
- Rural Female Labour Force Participation:
- Increased from 19.7% (2018-19) to 27.7% (2020-21).
Technological Innovation
- Semicon India Program:
- Budget of ₹76,000 crore to make India a global semiconductor hub.
- AI Impact:
- Expected to add $967 billion to the economy by 2035.
Social Justice and Gender Equality
- Nari Shakti Vandan Adhiniyam 2023: 33% reservation in Parliament.
- Beti Bachao Beti Padhao: Improved child sex ratios.
Defense Modernization
- Make in India in defense manufacturing reduces import dependency.
- Exports:
- Defense equipment worth ₹16,000 crore in FY 2022-23.
Urban Development
- Smart Cities Mission:
- Completed 90% of projects in 100 cities by July 2024.
Agricultural Modernization
- PM-KISAN Scheme:
- Over ₹2 lakh crore in direct benefits provided to farmers.
- Agri-exports:
- Expected to cross $50 billion in 2024-25.
Key Environmental Concerns
Deforestation and Habitat Loss
- Clearing forests for highways and urban projects disrupts ecosystems.
- Example: Hasdeo Aranya Forest (Chhattisgarh).
- FAO Report:
- India’s deforestation rate: 668 kha/year (2015-2020).
Air Pollution
- India has 39 of the world’s 50 most polluted cities (2023 IQAir Report).
- Cities like Delhi consistently exceed WHO PM2.5 standards.
Water Stress
- Over 70% of irrigated agriculture depends on groundwater.
- NITI Aayog Report:
- 600 million Indians face extreme water stress.
Land Degradation
- 30% of India’s land affected.
- Causes:
- Unsustainable land use.
- Exploitative agricultural practices.
Marine Pollution
- India produces 9.3 million tonnes of plastic waste annually.
- Coastal erosion affects 33.6% of India’s coastline (NCCR Study).
Climate Change
- India’s greenhouse gas emissions:
- 6.1% surge in 2023.
- Frequent extreme weather events:
- 85 days of such events in 2023.
Urban Waste Management
- India generates 62 million tonnes of waste annually.
- Example: Ghazipur landfill fire (2023).
Loss of Wetlands
- Nearly 40% of wetlands lost in the last 30 years (Wetlands International Study).
Strategies for Balancing Development and Conservation
Renewable Energy Transition
- Expand offshore wind and decentralized solar energy.
- Strengthen Renewable Purchase Obligation (RPO).
Sustainable Urbanization
- Promote green infrastructure and energy-efficient buildings.
- Integrate Smart Cities Mission with urban forestry and zero-waste policies.
Forest Conservation
- Enforce compensatory afforestation and community-driven projects.
- Use advanced satellite monitoring for forest cover.
Water Resource Management
- Adopt rainwater harvesting and drip irrigation.
- Develop ecologically sensitive river interlinking plans.
Circular Economy
- Encourage closed-loop production systems.
- Policies for waste segregation and composting.
Marine Protection
- Implement coastal regulation zones.
- Promote eco-tourism in fragile marine ecosystems.
Behavioral Change
- Public campaigns for energy conservation and waste reduction.
- Eco-literacy programs in schools.
Conclusion
India’s development aspirations, exemplified by the Ken-Betwa River Linking Project, underscore the need for sustainable strategies that preserve ecological integrity. Aligning growth with SDG 6, SDG 7, SDG 11, and SDG 13 will ensure a balanced approach to progress and environmental sustainability.




