India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC)
GK & Current Affairs for CLAT | CLAT Current Affairs 2026
Powered by CLAT Gurukul – Best online coaching for CLAT
Introduction
Connectivity is the backbone of modern geopolitics and global trade. In today’s interconnected world, control over trade corridors and supply chains translates into economic power and geopolitical influence. India’s ambitious India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC), announced at the G20 Summit in New Delhi in 2023, was conceived as a game-changing initiative to link South Asia, the Middle East, and Europe through rail, port, and digital infrastructure.
IMEC was envisioned not only as a trade corridor but also as a strategic counterweight to China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI). It was designed to reduce shipping times by nearly 40% compared to traditional routes via the Red Sea and the Suez Canal. It symbolized a rare geopolitical consensus among India, the United States, the European Union, Saudi Arabia, the UAE, Israel, and other partners in a region often torn by conflicts.
However, the ongoing Gaza war and wider Middle East instability have delayed progress on IMEC. The violence has disrupted diplomatic momentum, worsened Israel’s relations with Arab states, and shifted regional priorities back to security and conflict management rather than cooperation and economic integration.
For CLAT Current Affairs 2026, IMEC represents a critical case study combining international law, trade agreements, strategic diplomacy, and global governance. At CLAT Gurukul, the best online coaching for CLAT, we emphasize such issues because they directly connect law with international politics, providing aspirants a sharper understanding of the world they will be tested on.
Why in News?
- India’s National Security Council Secretariat recently hosted officials from the US, UAE, Saudi Arabia, France, Italy, Germany, Israel, Jordan, and the European Union to discuss IMEC’s progress.
- The Gaza conflict, which has killed over 61,000 people so far, has severely undermined the regional stability required to implement IMEC.
- Israel’s deteriorating ties with Jordan, Saudi Arabia’s hardened stance on Palestinian statehood, and the disruption of shipping in the Red Sea due to Houthi attacks have complicated IMEC’s execution.
- The future of IMEC remains uncertain, as stakeholders are unable to move forward on its original timelines and modalities.
Point-wise Summary of the Article
- The IMEC Plan
- Announced at G20 New Delhi Summit 2023.
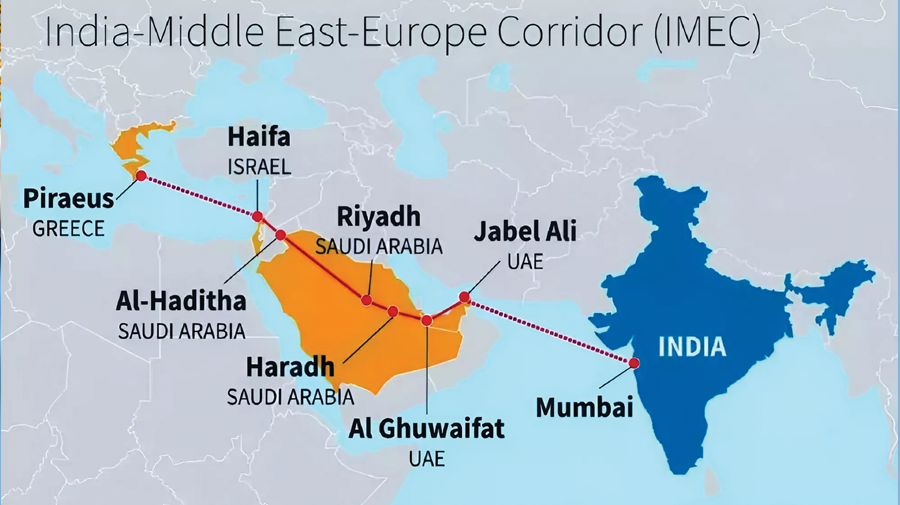
- Aims to connect India’s western ports to the UAE, then across Saudi Arabia and Jordan to Israel’s Haifa port.
- From Haifa, goods would be shipped to Greece and Italy, connecting to Europe’s railway networks.
- Envisions multiple components:
- High-speed freight railways.
- Cables for electricity and digital connectivity.
- Pipelines for clean hydrogen export.
- Trade facilitation for efficiency and job creation.
- Strategic Significance
- Offers an alternative to China’s BRI.
- Reduces dependency on the Suez Canal and Red Sea route.
- Symbolizes cooperation between India, Middle Eastern states, and Europe.
- EU is India’s largest trading partner ($137.41 billion in FY 2023–24).
- IMEC would deepen ties with the UAE and Saudi Arabia, where India’s trade has grown rapidly.
- Impact of the Gaza War
- Jordan-Israel relations have worsened due to pressure from Israel and the US on Jordan to absorb more Palestinians.
- Saudi Arabia is unwilling to normalize ties with Israel without concessions on Palestine.
- Instability in Gaza makes Arab states reluctant to proceed with Israel-centered projects.
- Houthi attacks on Red Sea shipping have vindicated IMEC’s logic but also raised costs.
- Other Geopolitical Obstacles
- Escalation of Israel’s war with Hezbollah in Lebanon, and tensions with Syria, Iraq, and Iran, complicate logistics.
- Regional rivalries (Qatar-GCC, Iran-Saudi, Arab states-Israel) remain unresolved.
- Lack of clear financing mechanisms has slowed implementation.
- Future Prospects
- IMEC’s western leg may not materialize soon, but eastern partnerships (India-UAE-Saudi Arabia) remain viable.
- Gulf states are already investing in India’s infrastructure, fintech, and energy sectors.
- Without Israel’s integration, however, IMEC’s strategic value is diluted.
Geopolitical Context
- China’s BRI vs. India’s IMEC
- BRI: China’s massive infrastructure program linking Asia, Africa, and Europe.
- IMEC: India’s counter-initiative, backed by the US and EU, promoting a rules-based connectivity alternative.
- Middle East Dynamics
- IMEC required Arab-Israel normalization.
- Gaza war reversed the trend, highlighting the fragility of regional diplomacy.
- India’s Stakes
- A chance to position itself as a key transit hub in global trade.
- Strengthen its energy security via Gulf ties.
- Gain recognition as a responsible global actor.
Notes on Peculiar Terms
- IMEC (India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor) – A planned trade corridor connecting India to Europe via the Middle East.
- BRI (Belt and Road Initiative) – China’s global infrastructure initiative spanning 140+ countries.
- Red Sea Route – Traditional maritime trade path linking Asia to Europe through the Suez Canal.
- Normalization – Diplomatic recognition and formal relations between countries (e.g., Israel and Arab states).
- Hydrogen Export Pipelines – Infrastructure to transport clean hydrogen, part of IMEC’s green energy focus.
- Houthi Attacks – Disruptions by Yemen’s Houthi rebels targeting Red Sea shipping lanes.
- Geopolitical Corridor – Trade routes that carry both economic and strategic significance.
Legal and Strategic Implications
- International Law
- IMEC represents a multilateral agreement among states, raising questions of sovereignty, trade regulation, and dispute resolution.
- Its suspension reflects how international law is often subordinated to geopolitics.
- India’s Foreign Policy
- IMEC boosts India’s Act West Policy complementing its Act East Policy.
- Positions India as a global connector bridging Asia and Europe.
- Security Challenges
- IMEC’s delay underlines the importance of peace and conflict resolution in international law.
- Trade corridors cannot function without secure borders and predictable diplomacy.
- Economic Law & Trade
- IMEC is linked to WTO principles of free trade and non-discrimination.
- Its realization could improve global supply chain efficiency, lowering costs for businesses.
Conclusion
The India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) was hailed as a historic project that could reshape global trade and strengthen India’s strategic influence. However, its progress has been stalled by the Gaza conflict, rising Arab-Israel tensions, and unresolved financing issues.
While the eastern leg of IMEC (India-UAE-Saudi Arabia) still holds potential, the western leg (via Israel to Europe) remains uncertain. The Gaza war underscores how fragile geopolitical agreements can be, and how law, diplomacy, and conflict resolution are inseparably tied to connectivity projects.
For CLAT Current Affairs 2026, IMEC is a vital case study of how global politics, international trade law, and strategic partnerships interact. At CLAT Gurukul, the best online coaching for CLAT, we train students to analyze such developments critically. Through online coaching for CLAT, aspirants learn not just facts, but also the legal, strategic, and economic implications that examiners expect in top answers.
This Blog is Powered by CLAT Gurukul — India’s Leading Law Entrance Prep Platform
At CLAT Gurukul, we believe in empowering future legal minds with the right blend of knowledge, strategy, and mentorship. This blog is a reflection of our commitment to quality content that not only helps aspirants stay updated but also sharpens their conceptual clarity.
Why CLAT Gurukul?
- Personalized Mentorship by Top Legal Educators
- Comprehensive Study Materials & Legal Updates
- Daily Practice Sets, Mocks & Performance Tracking
- Result-Oriented Strategy for CLAT, AILET, and CUET
Whether you’re reading this article to deepen your understanding or to stay ahead in your exam prep — you’re already one step closer with CLAT Gurukul by your side.
Join thousands of successful aspirants who trusted CLAT Gurukul and cracked India’s top law entrance exams.
Visit https://www.youtube.com/@CLATGurukul/shorts to learn more or speak to our experts now!
Note from CLAT Gurukul
At CLAT Gurukul, we are committed to providing free CLAT study material, including CLAT current affairs, legal reasoning practice sets, general knowledge updates, logical reasoning questions, English comprehension exercises, and more — all curated by top mentors.
Our blog section is regularly updated with high-quality CLAT content tailored to match the evolving pattern of the CLAT UG exam. Whether you’re looking for CLAT 2026 current affairs, CLAT legal reasoning passages, or mock practice sets, we have you covered.
We believe in open-access learning and will continue to publish free CLAT preparation resources to help serious aspirants succeed.
Explore more free content under categories like:
Best online coaching for CLAT, CLAT current affairs, CLAT GK updates, CLAT legal updates, CLAT logical reasoning, and CLAT English preparation.
For structured learning, daily mocks, and expert mentorship, visit https://www.youtube.com/@CLATGurukul/shorts — the Best CLAT Coaching in Patna and India’s most trusted platform for CLAT online coaching.




