Hydrology of the Brahmaputra – Strategic, Environmental & Legal Insights for CLAT 2026
Introduction
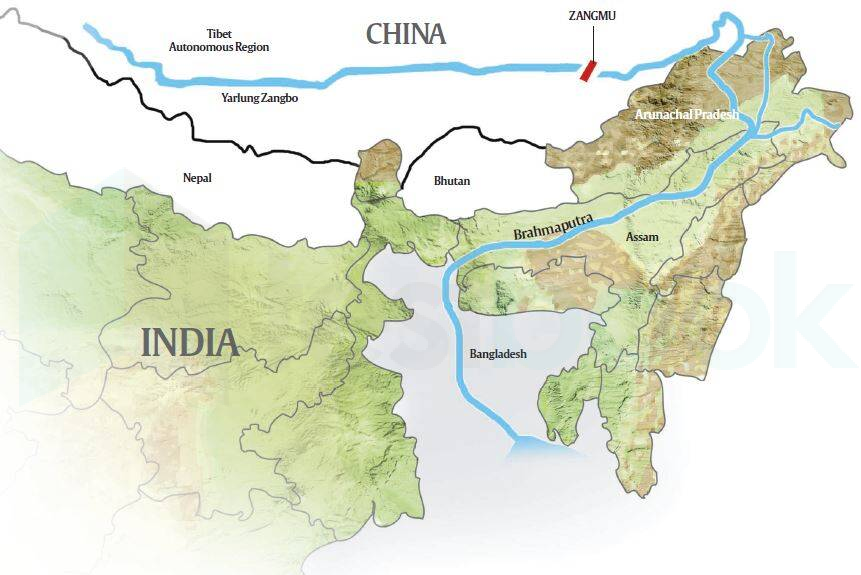
The Brahmaputra River, which originates in Tibet and flows through Arunachal Pradesh and Assam before entering Bangladesh, is both a lifeline and a geopolitical flashpoint. Recent discussions have sparked public concern over China’s dam-building activity upstream, particularly at Medog.
This article is essential for CLAT 2026 aspirants preparing for topics on transboundary water conflicts, hydrological policy, environmental law, and Indo-China strategic issues. Understanding the Brahmaputra’s role as a shared river system helps students explore its legal, ecological, and diplomatic dimensions.
Why in News
– Assam CM Himanta Biswa Sarma cautioned about Chinese dam construction on the Yarlung Tsangpo (Brahmaputra in Tibet).
– China is building the world’s largest hydroelectric project (Medog dam) on the river.
– The issue raises concerns for downstream states in India and Bangladesh, particularly over water availability and ecological consequences.
Point-wise Summary
- **Origin and Path of Brahmaputra**:
– Originates as Yarlung Tsangpo in Tibet, enters India in Arunachal Pradesh (called Siang), flows through Assam as Brahmaputra.
– After entering Bangladesh, it is called Jamuna.
2. **Chinese Dam Projects**:
– Medog Project: 60,000 MW capacity, three times larger than China’s Three Gorges Dam.
– Concerns: Reduced downstream flow, ecological imbalance, water security threats to India and Bangladesh.
3. **Rainfall Pattern in Basin**:
– India’s Brahmaputra Basin receives 4x more rainfall than the Tibetan Plateau.
– Monsoon-fed rivers dominate Indian side; Tibet contributes mainly snow-fed flow.
4. **Flow Contribution from Tibet**:
– Only 30% of Brahmaputra’s total flow comes from Tibet; remaining 70% comes from Indian rainfall.
– Rivers swell during monsoons in Arunachal and Assam due to heavy precipitation.
5. **Geostrategic Concerns**:
– Chinese infrastructure can manipulate river flow during conflicts or crises.
– India’s northeastern states are vulnerable due to lack of real-time data sharing.
6. **India’s Response Strategy**:
– Emphasis on multilateral diplomacy and satellite-based hydrological monitoring.
– Need for joint river management treaties and early warning systems.
– India must strengthen internal resilience via hydropower, storage, and flood control.
7. **Water Resource Development Potential**:
– Arunachal Pradesh has major untapped hydropower potential.
– Projects like Siang Basin Multipurpose Project proposed.
– Hindered by environmental issues and lack of local support.
8. **Other River Sharing Disputes**:
– Sutlej and Indus rivers also impacted by upstream Chinese activities.
– India needs comprehensive legal and environmental safeguards.
Explanation of Key Terms (Notes)
– **Yarlung Tsangpo**: Tibetan name of Brahmaputra River.
– **Medog Dam**: Proposed Chinese dam in Tibet, planned as world’s largest hydropower project.
– **Run-of-the-river Projects**: Hydroelectric systems that generate power without significant reservoir storage.
– **Hydrology**: The scientific study of the movement, distribution, and quality of water on Earth.
– **Transboundary River System**: A river that crosses one or more national boundaries.
– **Geostrategic Risk**: Strategic vulnerability arising from geographical and political factors.
– **Siltation**: Accumulation of silt in rivers, reducing water flow and reservoir efficiency.
Relevance for CLAT 2026 Aspirants
– **Transboundary Water Disputes**: Legal frameworks and international conventions.
– **Article 253**: Parliament’s power to legislate on international agreements.
– **Indus Waters Treaty model**: Precedent for Brahmaputra water diplomacy.
– **Environmental Law**: Legal provisions around large dam projects and their ecological impact.
– **Current Affairs 2026**: Strategic infrastructure and Indo-China relations.
Conclusion
The Brahmaputra’s hydrology is not merely a scientific matter—it is a subject of national security, environmental stability, and international diplomacy. India must balance its response through a mix of legal instruments, hydrological science, and strategic policy.
For CLAT 2026 students, this topic offers an integrated view of international law, environmental regulation, and constitutional powers—making it a vital part of their General Knowledge and Legal Reasoning preparation.