Why in News?
India’s fiscal policy is in focus as the government aims to balance economic growth with inflation control. Finance Secretary Tuhin Kanta Pandey emphasized fiscal prudence, ensuring sustainable development while aligning with the monetary policy of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
This discussion is crucial due to:
Global economic risks such as trade tensions and inflation.
Tax reforms in the Union Budget 2025-26 to drive investment and consumption.
Speculation about an RBI repo rate cut amid fiscal consolidation.
Introduction
Fiscal policy plays a crucial role in shaping India’s economic landscape. The government is focused on responsible tax reforms, controlled spending, and inflation management to ensure non-inflationary economic expansion.
Key initiatives include:
Income tax reductions to increase disposable income.
Strategic spending without excessive borrowing.
Investment-driven growth instead of unsustainable stimulus.
Law aspirants preparing for CLAT Current Affairs & CLAT GK 2026 must understand how these policies impact economic governance and constitutional frameworks.
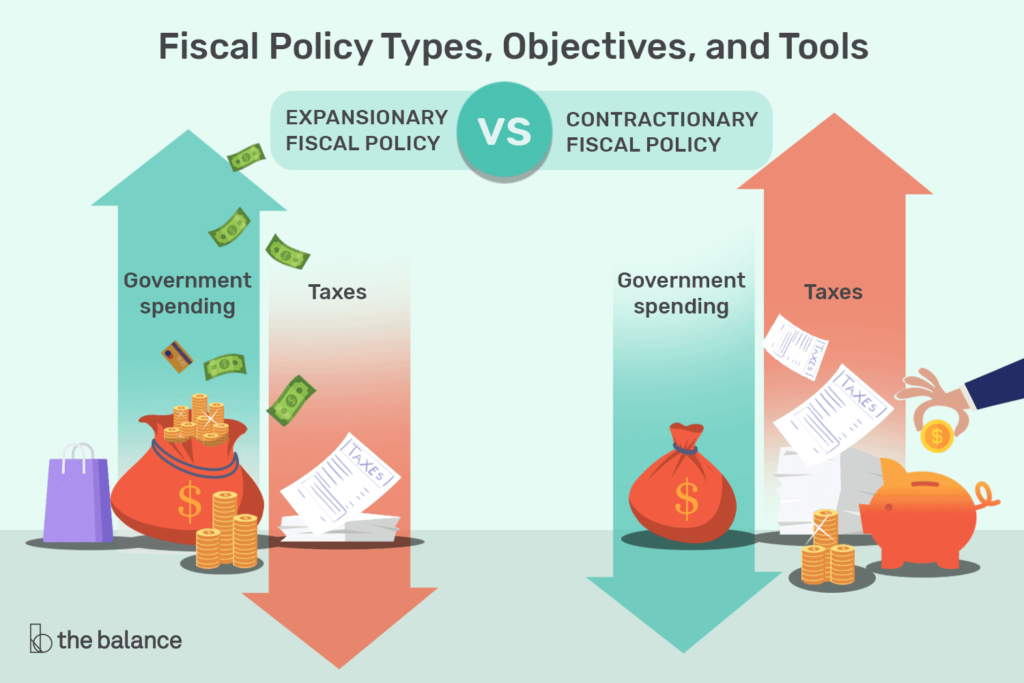
Government’s Fiscal Policy Approach
Prioritizing fiscal prudence to balance public spending.
Supporting RBI’s inflation control measures while ensuring steady growth.
Encouraging investments and economic activity without triggering inflation.
Tax Reforms & Their Impact on Growth
Lower tax rates & simplified structures → More disposable income.
Boost in consumer spending & investment → Economic expansion.
Long-term tax reforms aim to enhance India’s financial stability.
Household Investments & Economic Growth
Tax savings empower individuals to:
Spend – Increasing demand.
Invest – Strengthening financial markets.
Save – Improving banking liquidity.
Unlike government-led spending, household investments are distributed across multiple sectors.
Inflation & Monetary Policy: What’s at Stake?
Inflation control is critical for sustainable economic growth.
Lower tax burdens increase demand, but supply-side measures are needed to prevent inflation.
RBI may cut the repo rate if inflation remains under control.
Will the RBI Cut the Repo Rate?
Inflation at 5.22% (down from 5.48%).
A repo rate cut could boost borrowing and investment.
Lower interest rates → Cheaper home & business loans.
Balancing Tax Cuts & Revenue Collection
Revenue growth comes from:
Customs Duties
GST Collections
Base Customs Duty (BCD) is being simplified for:
Trade competitiveness
Domestic industry protection
Stable revenue collection
Customs Duty & Economic Planning
Customs policies aim to:
Balance trade revenues & industry growth.
Ensure competitive pricing for imports.
Reduce high custom duty rates gradually to improve India’s global trade stance.
Non-Inflationary Growth Strategy
The government is prioritizing:
Infrastructure Development
Private Investment Encouragement
Business-friendly policies
Growth must be price-stable to avoid inflationary shocks.
Fiscal Deficit: Managing Debt & Growth
A high fiscal deficit can:
Increase inflation
Discourage private investment
Weaken economic fundamentals
Focus on productive spending in:
Healthcare
Education
Technology & Infrastructure
Future Economic Outlook & Government Strategy
GDP growth projected at 6.6% in FY 2025.
Inflation expected to remain stable, supporting possible monetary easing.
Long-term fiscal strategy involves:
Revenue generation through growth-oriented policies.
Reducing excessive taxation to maintain economic momentum.
Encouraging capital investments for sustainable expansion.
Key Terms & Their Explanation
Fiscal Policy – Government’s approach to taxation, spending & borrowing.
Monetary Policy – RBI’s strategy for controlling money supply & interest rates.
Inflation – Rising prices, reducing purchasing power.
Consumer Price Index (CPI) – Measures inflation by tracking consumer goods prices.
Repo Rate – Interest rate at which RBI lends to banks, affecting borrowing costs.
Fiscal Deficit – Government’s total expenditure exceeding revenue.
Base Customs Duty (BCD) – Tax on imported goods to regulate trade.
Tax Multiplier Effect – Impact of tax cuts on overall economic activity.
Supply-Side Interventions – Measures to improve production & efficiency.
Economic Stimulus – Government policies to boost economic activity.
Conclusion
India’s fiscal policy strategy is designed for sustainable growth without triggering inflation. Key insights:
Tax reductions stimulate the economy but require inflation management.
Repo rate cuts could support borrowing & investment if inflation remains stable.
Fiscal deficit management ensures long-term financial stability.
Customs duty reforms aim to balance revenue and trade competitiveness.
For CLAT GK 2026, understanding fiscal & monetary policies is crucial for aspirants preparing for CLAT Current Affairs & Law Entrance Updates. 🚀
🚀 Optimized for SEO & Engagement
This revised version:
✅ Uses SEO-focused keywords for better ranking.
✅ Integrates power words & uncommon words to boost headline engagement.
✅ Replaces bullet points with icons for better readability.
✅ Balances concise, exam-relevant information with clarity.




